The area around the eye is referred to as the orbit. It is home to the muscles, nerves, fat, and blood vessels around the eyes. In rare cases, abnormal growths, referred to as orbital tumors, can develop in this space. They can impact your vision, eye movement, and appearance. Sometimes you may notice symptoms that indicate you have a tumor. In other cases, a tumor is discovered during an eye exam. In either case, you must get a proper diagnosis to determine whether your tumor is benign or cancerous. You may wonder, what percentage of orbital tumors are cancerous? Below, you will find the answer to this question, as well as additional helpful information about your risk of orbital tumors and how to receive the right treatment.
What Percentage of Orbital Tumors are Cancerous?
Orbital tumors can affect people of all ages. Because the orbit is such a small and delicate area, even a small tumor can cause serious issues. Early diagnosis and treatment from an expert are essential. Oculoplastic surgeons are trained to safely and effectively treat and diagnose complex growths. Conservative treatments may be used. But in some cases, orbital tumor surgery is necessary.
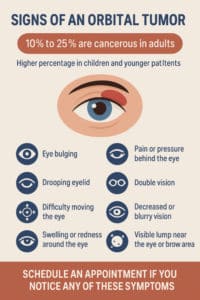
The good news is that most orbital tumors are not cancerous. Research shows that roughly 10% to 25% are cancerous in adults. The percentage is slightly higher in children and younger patients. Cancerous tumors are a cause for medical concern because they can spread to other areas. The cancer can spread to impact your eye, sinuses, and other parts of the body.
The vast majority of orbital tumors are benign. However, these tumors can still cause unwanted symptoms. Common symptoms include discomfort and vision issues. Unlike cancerous tumors, benign tumors do not spread to other parts of your body. If you have an orbital tumor, a biopsy or imaging test is necessary to determine if it is cancerous. Early intervention from an oculoplastic surgeon can improve patient outcomes.
Signs and Symptoms of an Orbital Tumor
The orbit of the eye is a very small space. As a result, even the smallest tumors can cause noticeable symptoms. Some signs appear gradually over time, while others may occur more suddenly. Below are some of the common signs of an orbital tumor.
- Eye bulging
- Pain or pressure behind the eye
- Drooping eyelid
- Double vision
- Difficulty moving the eye
- Decreased or blurry vision
- Swelling or redness around the eye
- Visible lump near the eye or brow area
If you experience any of the above symptoms, schedule an appointment immediately. A detailed eye exam and imaging can help determine the cause. Avoid waiting due to the risks associated with untreated orbital tumors.
Risk Factors for Orbital Tumors
Orbital tumors are rare. Still, there are certain factors that can increase the risk of developing one.
Age
Age plays a big role in the types of orbital tumors that may develop. Children typically develop tumors that grow quickly and require urgent care. Adults, in contrast, often develop tumors that grow more slowly and have a higher likelihood of being benign. No matter whether a tumor is benign or cancerous, you should seek treatment right away if you notice any unusual eye symptoms. Early detection results in better outcomes for both children and adults.
Genetic Conditions
Some people are born with genetic conditions that raise their risk for developing orbital tumors. If you or a family member has a known genetic condition, discuss it with an oculoplastic surgeon. They can share information about screening and early signs to watch out for. Regular eye exams are essential for individuals at higher risk due to genetic conditions.
Prior Cancer Diagnosis
If you have had cancer in the past, you may be at a higher risk of developing an orbital tumor. This is especially true if you had breast, lung, or prostate cancer. Cancer cells can travel through the bloodstream and grow in the soft tissue surrounding the eye. In many cases, the tumor causes noticeable symptoms, such as eye bulging, double vision, or eye pain. Even if you are being treated or are cancer-free, consult with a medical professional about any new symptoms. An oculoplastic surgeon can help you evaluate if the changes are related to the prior cancer diagnosis.
Immune System Issues
Your immune system is a crucial component in fighting off infections and abnormal cell growth. When it is weakened by illness, certain medications, or certain medical conditions, you are at an increased risk of orbital tumors. If your immune system is compromised, regular eye exams are even more important. Seek medical treatment right away if you notice any changes in your vision or the appearance of movement in your eyes.
Orbital Tumor Surgery
An oculoplastic surgeon performs surgery for orbital tumors. They are trained in both plastic surgery and eye care. This makes them uniquely qualified to operate on the delicate area around the eyes. Conservative treatment may be an option if there is no serious cause for medical concern. However, if the tumor is not responding to treatment or your symptoms get worse, surgery may be necessary. Surgery is often recommended when the tumor causes vision problems, is cancerous, or causes several unwanted symptoms. It may also be removed if a biopsy is needed to determine if the tumor is cancerous.
The type of surgery depends on the tumor’s size, location, and whether it is cancerous. Some surgeons involve a small incision in the eyelid or eyebrow. More extensive surgery may be needed in certain circumstances. The oculoplastic surgeon will provide you with all of the necessary information at your consultation. The top priority in surgery is to remove the tumor safely while protecting your eye, vision, and appearance. Your recovery timeline can vary depending on the extent of the surgery. Many patients are back to their routine within two weeks.
Protect Your Eye Health Today
If you have symptoms of an orbital tumor, contact the team at Taban MD Oculoplastic Surgery today to schedule a consultation.